Description
NIRS - NIRScout Extended System - MRI-compatible NIRS device
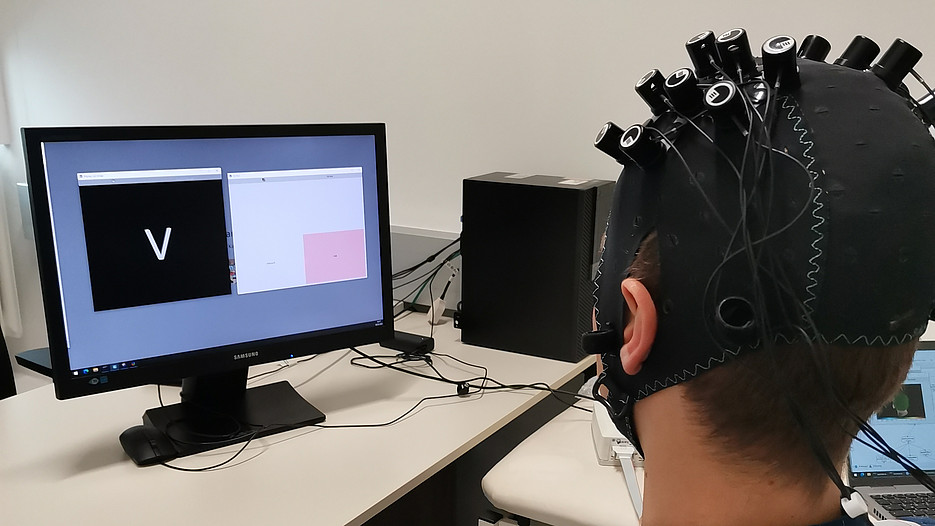
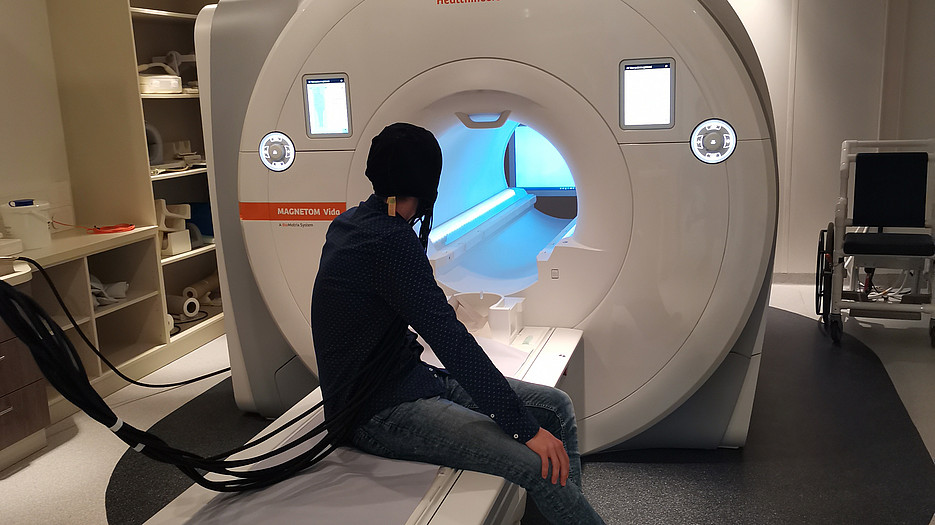
Near-infrared spectroscopy is a non-invasive, optical method for measuring brain metabolism. The NIRScout Extended System (MES Forschungssysteme GmbH, NIRx) is available in the laboratory for recording the relative concentration changes of oxygenated, deoxygenated and total haemoglobin in the blood in the upper layers of the cerebral cortex. The change in cerebral blood volume can be recorded simultaneously at different points. Frequency-modulated near-infrared light is emitted using optodes (emitters) placed on the scalp, thus enabling non-invasive and stress-free measurement. This light passes through the scalp, the skull and the upper layers of the cortex. It is then absorbed by the haemoglobin in the blood, reflected back depending on the oxygenation and collected again by the optodes (detectors). With the help of the measured changes in cerebral blood volume, activity in the brain can be inferred.
Features
- 16 LASER sources and 16 avalanche photodiode detectors
- MRI-compatible: synchronous MRI-NIRS measurements are possible
- LED and laser operation possible
- Additional short-distance channels to minimize artefacts
- Real-time processing of the NIRS signal possible (for BCI/neurofeedback applications)
- The measurement is non-invasive and causes minimal discomfort for the person being examined.
- The subject is not restricted by the measurement and the stimuli can be chosen relatively freely.
- The system is compact, i.e. it can be moved within the laboratory for possible combination measurements (virtual reality).
- Recording and evaluation software available
Further equipment
Measuring booth
The NIRS measurement is carried out in a sound and electromagnetically shielded measuring cabin from Soundblocker.
Other devices
Small, portable NIRS systems (NIRSPort and NIRSport 2, MES Forschungssysteme GmbH, NIRx, Department of Neuropsychology)